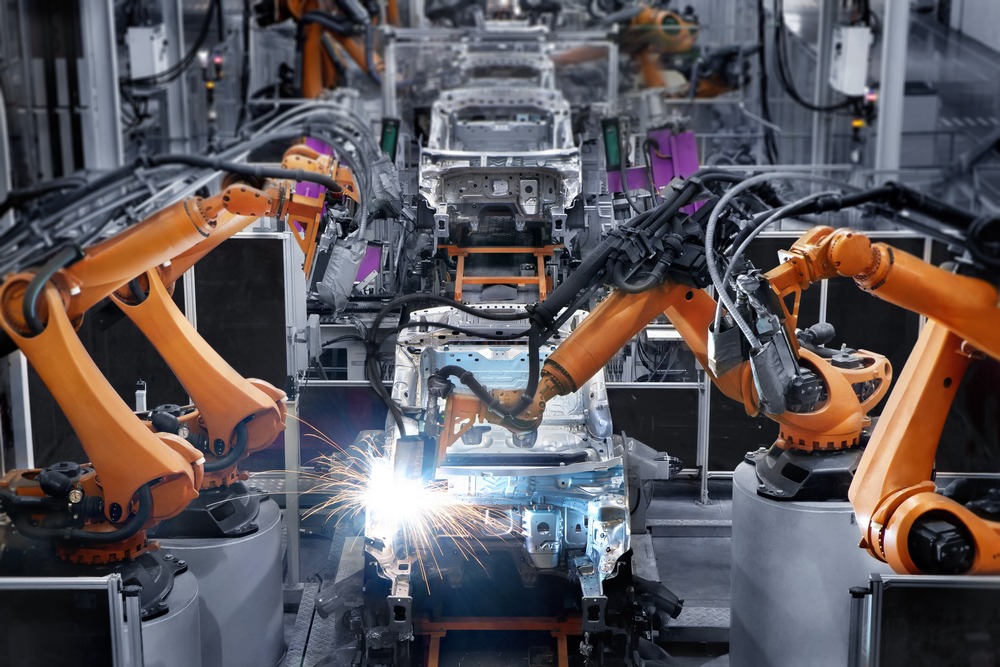
Welding has always been a cornerstone in the automotive industry, crucial for assembling various vehicle components and ensuring structural integrity. As the industry evolves, new trends and technologies in welding are emerging, enhancing efficiency, quality, and sustainability. This article explores the latest trends in welding applications within the automotive sector.
Lightweight Materials and Welding Techniques
1. Aluminum Welding: Aluminum has become increasingly popular in automotive manufacturing due to its lightweight properties, which contribute to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. However, welding aluminum presents challenges such as high thermal conductivity and a tendency to form oxides. Recent advancements include:
- Friction Stir Welding (FSW): This solid-state joining process is ideal for welding aluminum, offering high strength and minimal distortion.
- Laser Welding: Laser welding provides precise control and deep penetration, making it suitable for thin aluminum sheets and complex geometries.
2. High-Strength Steel: High-strength steel (HSS) is used to enhance vehicle safety and performance without significantly increasing weight. Welding HSS requires specialized techniques to maintain its mechanical properties:
- Resistance Spot Welding (RSW): Widely used for joining HSS in body-in-white (BIW) assemblies, RSW offers high productivity and strong joints.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): Advanced GMAW techniques, such as pulsed arc welding, provide better control and reduced heat input, preserving the strength of HSS.
Advanced Welding Processes
1. Laser Welding: Laser welding is becoming more prevalent in automotive manufacturing due to its precision and efficiency. It is particularly useful for high-volume production and complex assemblies:
- Remote Laser Welding: This technique allows for welding at a distance, enabling greater flexibility and speed in the welding process. It is ideal for difficult-to-reach areas and intricate components.
- Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding: Combining laser and arc welding techniques, this method offers the benefits of both processes, such as deep penetration and high welding speeds.
2. Friction Stir Welding (FSW): FSW is increasingly used for joining non-ferrous metals and mixed materials, such as aluminum to steel. Its advantages include:
- Superior Joint Quality: FSW produces defect-free welds with excellent mechanical properties.
- Energy Efficiency: The process is energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, producing no fumes or emissions.
3. Cold Metal Transfer (CMT): CMT is a modified GMAW process that offers precise control of heat input, making it ideal for welding thin materials and dissimilar metals. Benefits include:
- Minimal Spatter: CMT produces clean welds with minimal spatter, reducing post-weld cleaning and finishing.
- Reduced Distortion: The controlled heat input minimizes thermal distortion, improving weld quality and dimensional accuracy.
Automation and Robotics
1. Robotic Welding: The use of robotic welding systems in the automotive industry is growing, driven by the need for efficiency, consistency, and quality:
- Flexibility: Robotic systems can be programmed for a variety of welding tasks, from spot welding to arc welding, enabling quick changeovers and high flexibility.
- Precision: Robots provide high precision and repeatability, ensuring consistent weld quality across large production runs.
- Safety: Automation reduces human exposure to hazardous welding environments, enhancing workplace safety.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human welders, enhancing productivity and safety:
- Ease of Use: Cobots are user-friendly and can be easily integrated into existing workflows, requiring minimal training.
- Versatility: Cobots can assist with various tasks, from welding to material handling, improving overall efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Quality Control and Inspection
1. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): NDT techniques are crucial for ensuring weld quality without damaging the components. Advances in NDT include:
- Ultrasonic Testing: This method uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal defects, providing accurate and reliable results.
- X-Ray and Computed Tomography (CT): X-ray and CT scanning offer detailed imaging of welds, allowing for precise identification of defects and anomalies.
2. Digital Inspection Systems: Digital technologies are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of weld inspection:
- Machine Vision: Machine vision systems use cameras and image processing algorithms to inspect welds in real-time, identifying defects and ensuring quality.
- Laser Scanning: Laser scanning provides high-resolution, three-dimensional measurements of welds, enabling detailed analysis and quality assurance.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
1. Energy-Efficient Processes: Advancements in welding technology are contributing to more energy-efficient manufacturing processes:
- Eco-Friendly Welding Techniques: Processes like FSW and CMT are energy-efficient and produce minimal emissions, supporting sustainability goals.
- Optimized Welding Parameters: The use of advanced control systems allows for the optimization of welding parameters, reducing energy consumption and waste.
2. Recycling and Material Reuse: Welding plays a key role in the recycling and reuse of materials in the automotive industry:
- Repair and Reclamation: Advanced welding techniques enable the repair and reclamation of damaged components, extending their lifespan and reducing waste.
- Joining Recycled Materials: Welding processes are being adapted to join recycled materials, supporting circular economy initiatives and reducing the demand for virgin materials.
Conclusion
The automotive industry is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in welding technologies that enhance efficiency, quality, and sustainability. From the adoption of lightweight materials and advanced welding processes to the integration of automation and digital inspection systems, these trends are shaping the future of automotive manufacturing. As the industry progresses, staying abreast of these innovations will be crucial for manufacturers seeking to maintain a competitive edge and meet the demands of a rapidly changing market.