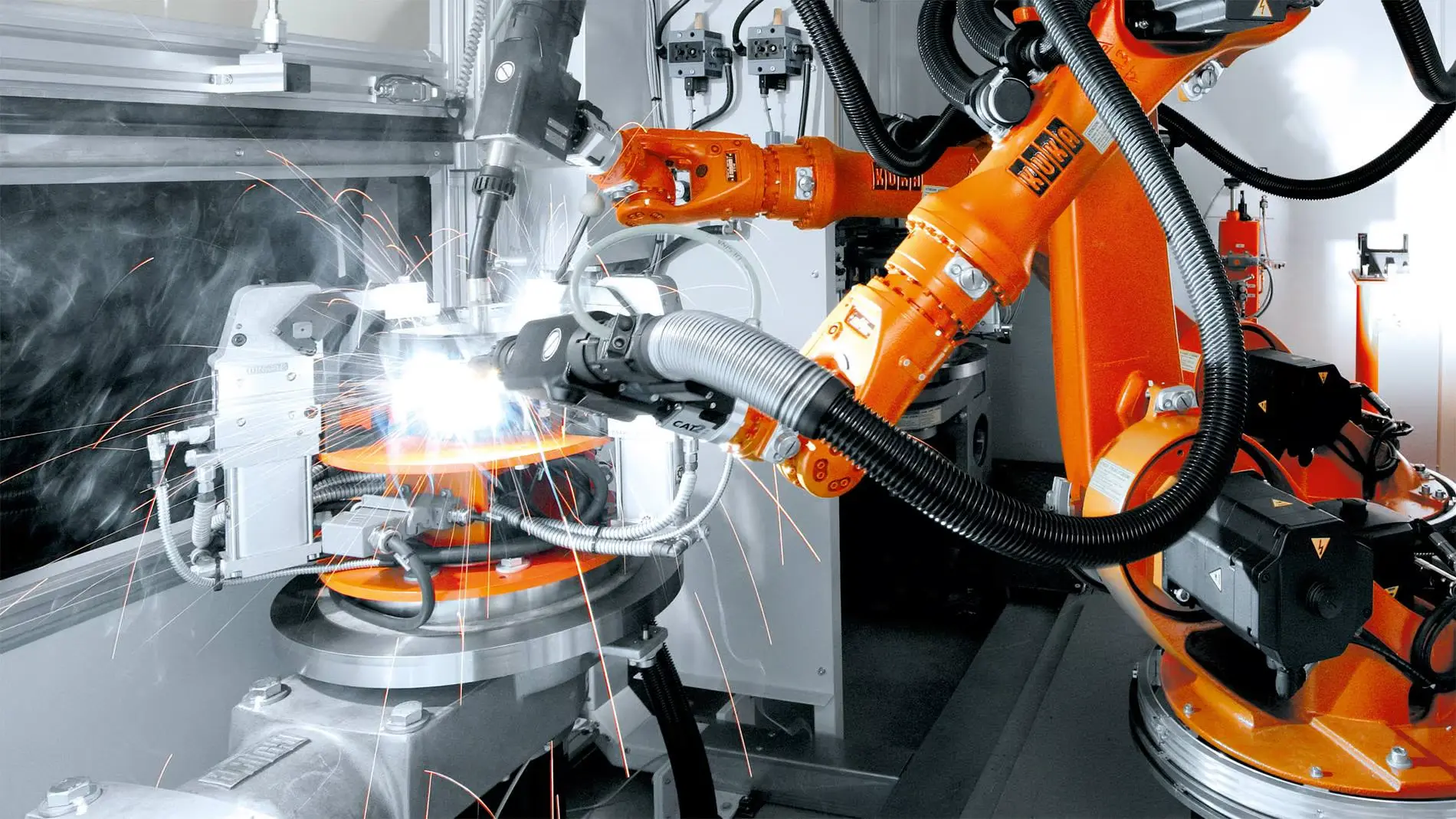
The welding industry, a cornerstone of manufacturing, construction, and repair, is experiencing a profound transformation with the integration of automation. Robots and automated systems are increasingly being employed to enhance efficiency, precision, and safety. This article explores the introduction of automation in welding, highlighting its benefits and challenges, and why it’s revolutionizing the industry.
The Rise of Automation in Welding
The adoption of automation in welding is driven by the need for higher productivity, consistent quality, and the ability to tackle complex projects that are difficult or impossible for manual welding. Automated welding systems, including robotic arms, automated welding cells, and advanced control systems, are becoming more common across various industries.
Benefits of Welding Automation
- Zwiększona produktywność
- Automated welding systems can operate continuously without fatigue, significantly increasing the throughput of welding operations. Robots can work around the clock, leading to higher production rates and shorter project timelines.
- Enhanced Precision and Consistency
- Automation ensures consistent quality by eliminating human error. Robotic welders follow programmed paths with high precision, producing uniform welds with minimal variation. This consistency is crucial for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is paramount.
- Improved Safety
- Welding is a hazardous job, involving exposure to intense light, heat, and toxic fumes. Automation reduces the risk to human welders by performing dangerous tasks and minimizing direct exposure to harmful conditions. This leads to a safer working environment and reduces the incidence of work-related injuries.
- Efektywność kosztowa
- While the initial investment in automated systems can be substantial, the long-term benefits include reduced labor costs, lower material wastage, and fewer reworks due to defects. Over time, these savings can offset the initial costs and lead to higher profitability.
- Flexibility and Scalability
- Modern automated welding systems are highly adaptable and can be reprogrammed for different tasks. This flexibility allows manufacturers to quickly switch between different projects or product lines without extensive downtime. Additionally, scaling up production is easier with automation, as additional robotic units can be integrated into the workflow.
Challenges of Welding Automation
- Wysoka inwestycja początkowa
- The cost of purchasing and installing automated welding systems can be prohibitive for small and medium-sized enterprises. This includes the expense of robots, control systems, software, and training for operators and maintenance staff.
- Complex Integration
- Integrating automation into existing manufacturing processes can be complex. It requires careful planning, customization, and synchronization with other parts of the production line. Failure to properly integrate can lead to inefficiencies and increased downtime.
- Skilled Workforce Requirements
- Automation does not eliminate the need for skilled workers; rather, it shifts the demand to different skill sets. Operators and maintenance personnel must be trained to program, monitor, and troubleshoot automated systems. This necessitates ongoing training and education.
- Maintenance and Downtime
- Automated systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Unplanned downtime due to system failures can be costly and disrupt production schedules. Having a robust maintenance plan and quick access to spare parts is essential to minimize downtime.
Real-World Applications of Welding Automation
- Przemysł motoryzacyjny
- The automotive industry has been a pioneer in adopting welding automation. Robotic welders are used extensively to assemble car bodies, frames, and other components with high precision and speed. Automation ensures the structural integrity and safety of vehicles while meeting high production demands.
- Lotnictwo i kosmonautyka
- In the aerospace industry, where the quality and precision of welds are critical, automation plays a key role. Automated systems are used to weld complex components such as turbine blades, aircraft frames, and fuel tanks, ensuring that they meet stringent industry standards.
- Construction and Infrastructure
- Large-scale construction projects benefit from automated welding through the efficient production of steel structures, pipelines, and bridges. Automation enables faster project completion while maintaining high-quality welds.
- Shipbuilding
- The shipbuilding industry utilizes automated welding for the construction of hulls, decks, and other critical components. Automation enhances the efficiency of shipbuilding operations and ensures the durability and safety of vessels.
The Future of Welding Automation
The future of welding automation looks promising, with ongoing advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. These technologies will further enhance the capabilities of automated systems, allowing for smarter, more adaptive welding processes. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are emerging as a trend, working alongside human welders to combine the precision of automation with the flexibility and decision-making skills of humans.
Moreover, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and real-time data analytics will enable predictive maintenance, process optimization, and improved quality control. As technology continues to evolve, the barriers to entry for welding automation will decrease, making it more accessible to a broader range of industries and businesses.
Wnioski
Automation in welding processes is transforming the industry by increasing productivity, improving precision, enhancing safety, and reducing costs. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, making automation an attractive investment for forward-thinking companies. As technology continues to advance, the role of automation in welding will only grow, paving the way for a future where human welders and automated systems work together to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and quality.