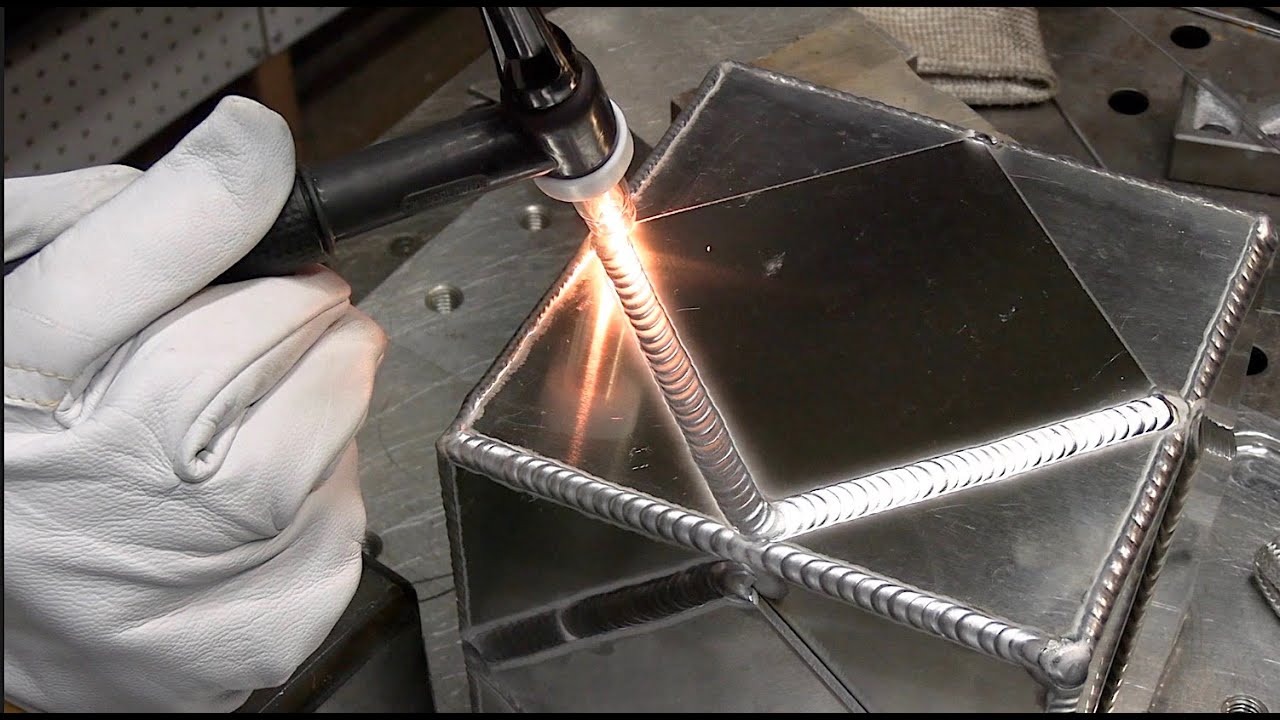
Aluminum welding presents unique challenges and demands specific techniques to achieve strong, reliable welds. As a lightweight and versatile metal, aluminum is increasingly used in various industries, from aerospace to automotive and beyond. However, its properties, including high thermal conductivity and susceptibility to oxidation, complicate the welding process compared to steel or other metals. This article explores the complexities of welding aluminum, discusses common challenges encountered by welders, and outlines best practices to ensure successful outcomes.
Understanding Aluminum Welding
Aluminum alloys are broadly categorized into two groups: heat-treatable and non-heat-treatable. Each group requires different welding approaches due to variations in alloy composition and properties. Heat-treatable alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, derive their strength from heat treatment after welding. In contrast, non-heat-treatable alloys, like 3003 and 5052, cannot be strengthened significantly by heat treatment post-welding.
Challenges in Aluminum Welding
- High Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity means heat dissipates quickly from the weld zone, requiring higher welding currents and travel speeds to maintain proper penetration and fusion.
- Oxide Formation: Aluminum rapidly forms an oxide layer when exposed to air, which melts at a much higher temperature than the aluminum itself. This oxide layer must be removed before welding to ensure a clean weld pool and strong joint.
- Cracking Susceptibility: Aluminum alloys are prone to hot cracking, particularly in heat-affected zones, due to their narrow melting range and sensitivity to weld cooling rates.
- Poroznost: Hydrogen and other contaminants can easily become trapped in the weld pool, leading to porosity issues that compromise weld strength and integrity.
Best Practices for Aluminum Welding
- Priprava materiala: Proper cleaning and preparation of aluminum surfaces are crucial. Remove oxide layers using stainless steel wire brushes or chemical cleaning methods before welding.
- Welding Technique: Use AC (alternating current) for welding aluminum to effectively clean the oxide layer and ensure good arc stability. Adjust welding parameters such as amperage, voltage, and travel speed according to material thickness and alloy type.
- Zaščitni plin: Use high-purity argon or helium-based shielding gases to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. Gas flow rates and coverage must be optimized to prevent oxidation during welding.
- Joint Design: Employ joint designs that facilitate heat dissipation and minimize stress concentrations. Chamfer or bevel thick aluminum sections to ensure proper weld penetration and reduce the likelihood of defects.
- Obdelava po varjenju: For heat-treatable alloys, follow recommended post-weld heat treatment procedures to restore or enhance mechanical properties. Non-heat-treatable alloys benefit from stress-relieving processes to reduce residual stresses.
- Quality Control: Implement rigorous inspection techniques, such as visual inspection, dye penetrant testing, or radiographic testing, to detect potential defects early and ensure weld quality meets required standards.
Zaključek
Welding aluminum alloys demands precision, expertise, and adherence to specialized techniques. Understanding the metallurgical properties and challenges associated with aluminum is crucial for achieving high-quality welds that meet structural and performance requirements. By following best practices in material preparation, welding technique, and post-weld treatment, welders can overcome these challenges and produce durable, reliable aluminum welds across various industrial applications.
In conclusion, while welding aluminum poses significant challenges, employing proper procedures and techniques ensures successful outcomes, reinforcing its role as a vital material in modern manufacturing and construction.